We expect to see these new CPU cores in MediaTek Dimensity 9300, Samsung Exynos 2400, and Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 processors later this year or early next year. The Galaxy S24 series is expected to feature the Exynos 2400 and the Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 chips.
ARM Cortex-X4, Cortex-A720, and Cortex-A520 CPU cores bring higher power efficiency and performance
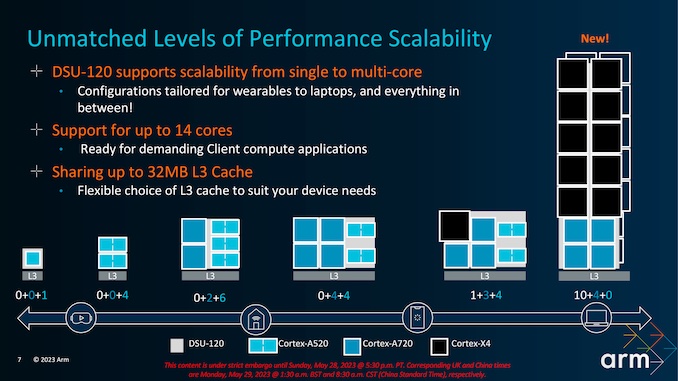
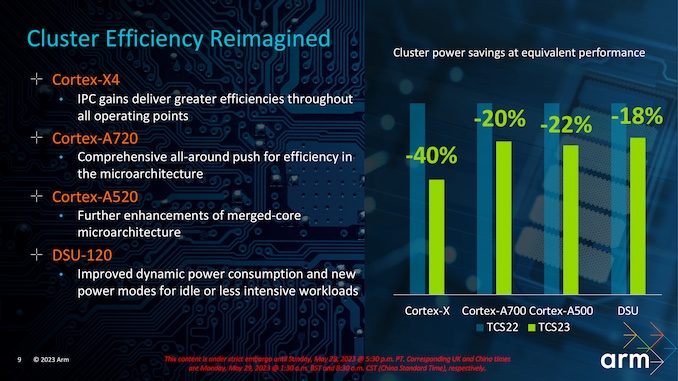
All new CPU cores from ARM are 64-bit-only, which means they won't support 32-bit applications. The processors using ARM's DSU-120 (DynamIQ Shared Unit 120) design can feature up to 14-core CPUs, which means they can also be a great fit for PCs and laptops. However, in the smartphone ecosystem, we could see brands like MediaTek, Qualcomm, and Samsung using a 1+5+2 (1x Cortex-X4 + 5x Cortex-A720 + 2x Cortex-A520) design for their octa-core processors. Compared to last year, ARM is claiming a CPU performance jump of 27% in multi-threaded tasks.
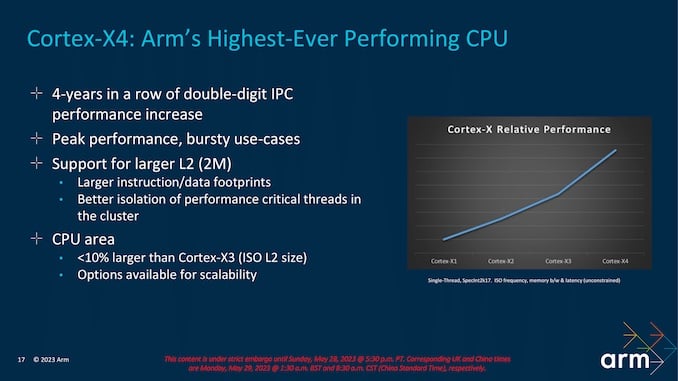
ARM also claims that its Cortex-X4 CPU core is 40% more power efficient than Cortex-X3. The Cortex-X3 is used in chips like the Dimensity 9200 and the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2. It means that chips using the Cortex-X4 CPU core will be a lot more power-efficient when performing high-end tasks like camera, gaming, and multitasking. The Cortex-A520 core is 22% more power-efficient, while the Cortex-A720 is around 20% more power-efficient than their predecessor cores. Overall, this should improve the battery life of smartphones.
The ARM Cortex-X4 offers a considerable improvement in performance and battery efficiency, and it will be used in high-end smartphones and tablets. It can go as high as 3.4GHz and has a 2MB L2 cache (2x compared to last year).
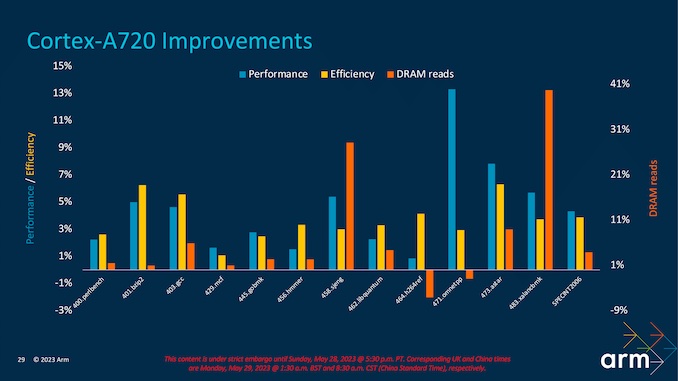
With the Cortex-A720, ARM's focus is to offer maximum sustained performance with higher efficiency. Cortex-A720 CPU cores are as small as Cortex-A78 from a few years ago while still offering 10% more performance. We could see this CPU core used in more mid-range and low-end chips. Overall, ARM expected around 15% faster performance compared to previous generations.
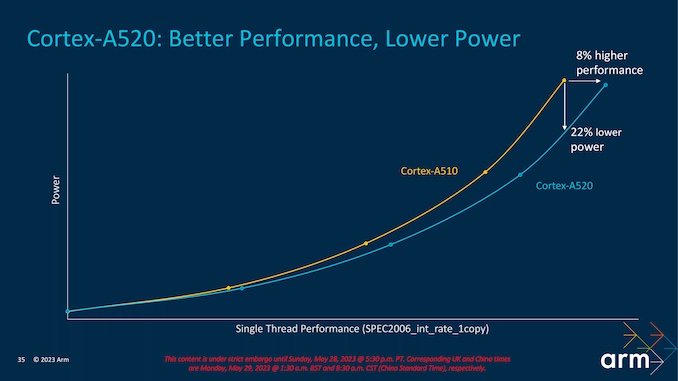
The Cortex-A520 CPU core, which is used for smaller and low-intensity tasks, offers 22% more power efficiency than last year's Cortex-A510. At the same level of power consumption, Cortex-A520 cores can offer 8% more performance than Cortex-A510 cores. Overall, we could see future Android smartphone chipsets move to a 64-bit-only architecture and offer improved performance, power efficiency, and security with ARM's TS23 designs.
These performance and efficiency improvements would come to the Galaxy S24, Galaxy S24+, Galaxy S24 Ultra, and the Galaxy Tab S10 series.
ARM's Immortalis G720 GPU offers much-improved ray-tracing performance
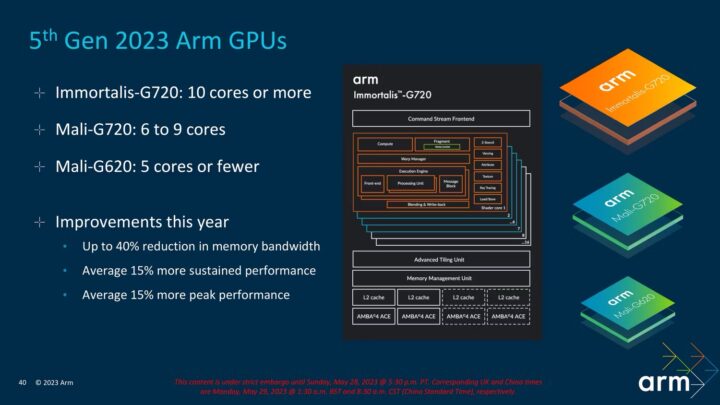
ARM also unveiled the Immortalis G720 GPU for high-end smartphone and tablet processors. It offers 52-67% higher performance in ray-tracing tasks and 5-52% improved performance in VRS (Variable Rate Shading) tasks compared to competing GPUs. This new GPU claims to offer higher performance and power efficiency for longer gaming sessions. The Immortalis G720 GPU can have 10 or higher cores.
Based on the same fifth-generation graphics, the Mali-G720 GPU will be used in mid-range smartphones, while the Mali-G620 GPU is for entry-level smartphones. The Mali-G620 GPU can have five or fewer cores, while the Mali-G720 GPU can have 6-9 cores. All of ARM's new GPUs claim to have around 15% better power efficiency, leading to improved battery life while gaming.
Since Samsung (System LSI) is using AMD Radeon-based Xclipse GPUs in its Exynos processors, we don't expect the company to use ARM's Immortalis-G720, Mali-G720, or Mali-G620 GPU in its future chips for phones, tablets, and wearables.